The world of electronics is evolving at a rapid pace, with devices becoming smaller, faster, and more powerful each year. At the heart of this transformation lies a critical component that makes all of it possible: the PCB board (Printed Circuit Board). Often overlooked, the PCB is the unsung hero of modern electronics. Without it, none of the devices we rely on—smartphones, computers, medical devices, automotive systems—would function as they do.
Contents
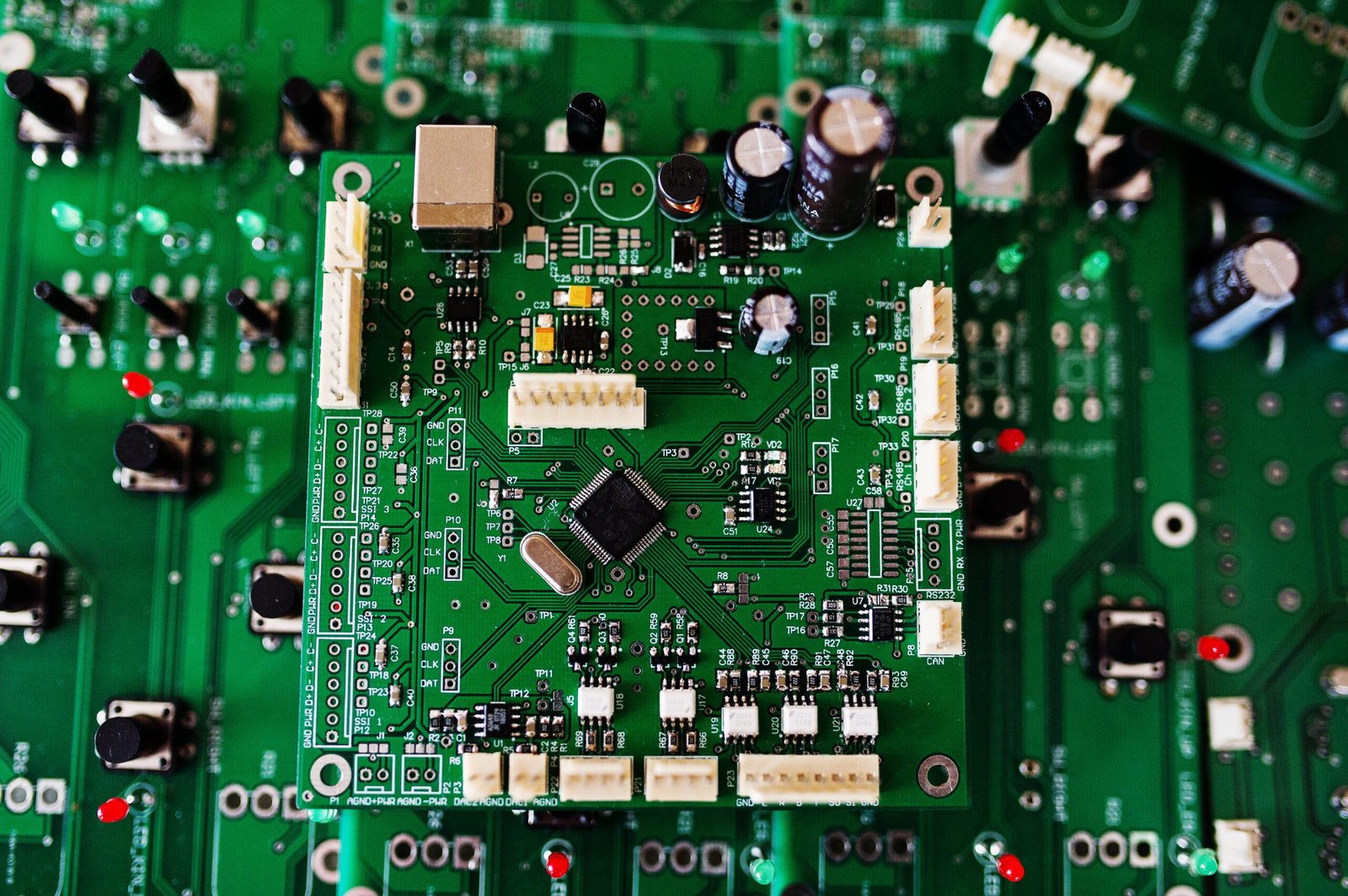
What is a PCB Board?
A PCB board is a flat, rigid platform that physically supports and connects electronic components within a circuit. Typically constructed from non-conductive materials like fiberglass or composite resin, the PCB contains conductive pathways, or traces, that link various components such as resistors, capacitors, microchips, and connectors. These traces form the electrical circuit that allows current to flow and signals to be transmitted between the components, enabling the device to perform its intended function.
PCBs vary in complexity, from simple single-layer boards to multi-layer designs that support hundreds or even thousands of components. The design, material selection, and manufacturing process of a PCB board directly impact the performance, reliability, and durability of the final product.
The Importance of PCB Boards in Electronics
In the vast world of electronics, PCB boards are fundamental to the operation of virtually every device. The role of a PCB goes far beyond simply providing mechanical support; it serves as the electrical backbone that enables components to interact with each other. Let’s explore why PCBs are indispensable in the world of electronics:
- Space Optimization: One of the key advantages of using PCB boards is the ability to integrate complex circuits into small, compact designs. The layers of the PCB provide space-efficient solutions by allowing components to be mounted in tight spaces, reducing the overall size of the device. This compactness is crucial in modern electronics, where portability and miniaturization are paramount.
- Reliable Electrical Connectivity: PCBs ensure that electronic components are electrically connected in a precise and reliable manner. The conductive traces etched into the PCB allow electrical signals to flow seamlessly, ensuring that components work together as intended. Without PCBs, it would be incredibly difficult to achieve the same level of reliability and performance in a device.
- Cost-Effective Manufacturing: Compared to traditional methods of wiring electronic components by hand, PCB boards offer a much more efficient and cost-effective solution. The automated processes used in PCB manufacturing and assembly ensure that high-quality boards can be produced in large quantities, which helps reduce the overall cost of manufacturing electronic devices.
- Durability and Performance: PCB boards are designed to be durable and reliable, even in challenging environments. They are built to withstand heat, moisture, and mechanical stress, ensuring that the devices they power continue to operate reliably over time. This is particularly important in industries such as automotive, medical, and aerospace, where failure is not an option.
- Simplified Repair and Maintenance: When a component on a PCB fails, it can be replaced or repaired with ease, allowing for more cost-effective and efficient maintenance. Unlike older methods where the entire wiring of a device had to be replaced, PCBs allow for the selective replacement of faulty components, extending the life of the device.
The Different Types of PCB Boards
PCB boards come in a variety of types, each designed for specific applications. Depending on the complexity and requirements of the device, the type of PCB used can vary. Let’s take a look at the most common types of PCBs:
- Single-Layer PCB: The simplest form of PCB, with only one layer of conductive material. Single-layer PCBs are ideal for low-cost, simple electronic devices where space and complexity are not major concerns.
- Double-Layer PCB: These PCBs feature two layers of conductive material, allowing for more complex circuits and more efficient use of space. Double-layer PCBs are commonly found in consumer electronics like televisions, game consoles, and computers.
- Multi-Layer PCB: Multi-layer PCBs are more advanced and feature multiple layers of conductive material stacked on top of each other. These boards are used in high-performance electronics such as smartphones, laptops, and networking equipment, where higher density and complexity are required.
- Flexible PCB: Unlike traditional rigid PCBs, flexible PCBs are made from flexible materials such as polyimide. This allows the PCB to bend and conform to the shape of the device, making it ideal for wearable technology, medical devices, and other applications where flexibility is required.
- Rigid-Flex PCB: Combining both rigid and flexible components, rigid-flex PCBs are used in applications that require both stability and flexibility. These PCBs are commonly used in aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
The PCB Assembly Process
Once a PCB board is designed and fabricated, the next step is assembly, where the electronic components are placed and soldered onto the board. The assembly process involves several stages:
- Component Placement: The first step in PCB assembly is placing the components on the board. This is typically done using automated pick-and-place machines, which can precisely place components in their designated positions on the board.
- Soldering: After the components are placed, they are soldered onto the board. This process can be done using wave soldering for through-hole components or reflow soldering for surface-mount components. Soldering ensures that the components are securely attached to the PCB and form a reliable electrical connection.
- Inspection and Testing: After the PCB has been assembled, it undergoes various tests to ensure that all components are properly placed and functioning. This includes visual inspections, electrical testing, and, in some cases, X-ray inspection to detect any hidden defects or issues.
- Final Testing: Once the PCB has passed initial testing, it undergoes functional testing to ensure the entire circuit works as intended. This is particularly important for high-end devices where precision and reliability are critical.
At PCBINQ, we offer a comprehensive PCB assembly service that includes everything from parts procurement to final testing. We specialize in both low-volume and high-volume PCB assembly, with capabilities for multi-layer, rigid-flex, and custom PCBs. Our commitment to quality and rapid turnaround ensures that your projects are completed on time and to the highest standards. Visit www.pcbinq.com to learn more.
How to Choose the Right PCB Manufacturer
Selecting the right manufacturer for your PCB board is crucial to the success of your project. Here are some key factors to consider:
- Experience and Reputation: Choose a manufacturer with a proven track record in PCB design and assembly. Look for a company that has experience in producing the type of PCB you need and can handle complex designs.
- Quality Control: The manufacturer should have robust quality control processes in place to ensure that every PCB board meets industry standards. Certifications like IPC-A-610 and ISO 9001 are indicators of high-quality production.
- Turnaround Time: Depending on your project’s timeline, you may need a PCB manufacturer that offers quick turnaround times. At PCBINQ, we offer rapid prototyping services, with small-batch orders ready in 24–48 hours.
- Customization: The manufacturer should be able to provide customized solutions to meet your specific requirements. Whether you need a multi-layer PCB, flexible PCB, or rigid-flex PCB, the manufacturer should be able to accommodate your needs.
- Pricing: While price should not be the only factor in your decision, it is essential to choose a manufacturer that offers competitive pricing without compromising on quality. Transparent pricing with no hidden fees is crucial.
The Future of PCB Boards
As technology continues to advance, PCB boards will play an even more critical role in the development of future electronics. Emerging trends such as 5G technology, the Internet of Things (IoT), and wearable devices will drive demand for more advanced PCBs with greater performance capabilities. Additionally, there is growing interest in eco-friendly and sustainable PCB manufacturing, as manufacturers strive to reduce environmental impact by using recyclable materials and reducing waste.
Conclusion
In conclusion, PCB boards are the foundation of modern electronics, enabling devices to perform the complex tasks we rely on daily. From simple consumer electronics to advanced medical devices and industrial machinery, PCB boards are essential to ensuring that these devices operate efficiently and reliably. As technology continues to evolve, so too will the demands placed on PCBs, driving innovation in both design and manufacturing processes.
At PCBINQ, we are dedicated to providing high-quality PCB boards and assembly services to meet the growing needs of the electronics industry. Whether you need a prototype or are scaling up for mass production, we have the expertise and capabilities to support your project. Visit us at www.pcbinq.com to learn more about how we can help bring your ideas to life.